What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It affects how your body uses sugar. As a result, your blood sugar levels become higher than normal. This condition usually appears in the second or third trimester. However, it can affect both you and your baby’s health. Early detection and proper care are important for a healthy pregnancy. According to the CDC, gestational diabetes affects about 2% to 10% of pregnancies in the United States each year.
Common Symptoms
Often, gestational diabetes does not cause clear symptoms. Still, some women may notice signs. For example, you might experience:
Because symptoms can be mild or absent, regular screening during pregnancy is important.
Main Causes and Risk Factors
Gestational diabetes happens when your body cannot make enough insulin during pregnancy. Insulin is a hormone that helps control blood sugar. During pregnancy, your body makes more hormones and goes through changes. These changes can make it harder for insulin to work well. As a result, your blood sugar rises.
Several factors can increase your risk, such as:
Even if you have risk factors, you can take steps to lower your chances.
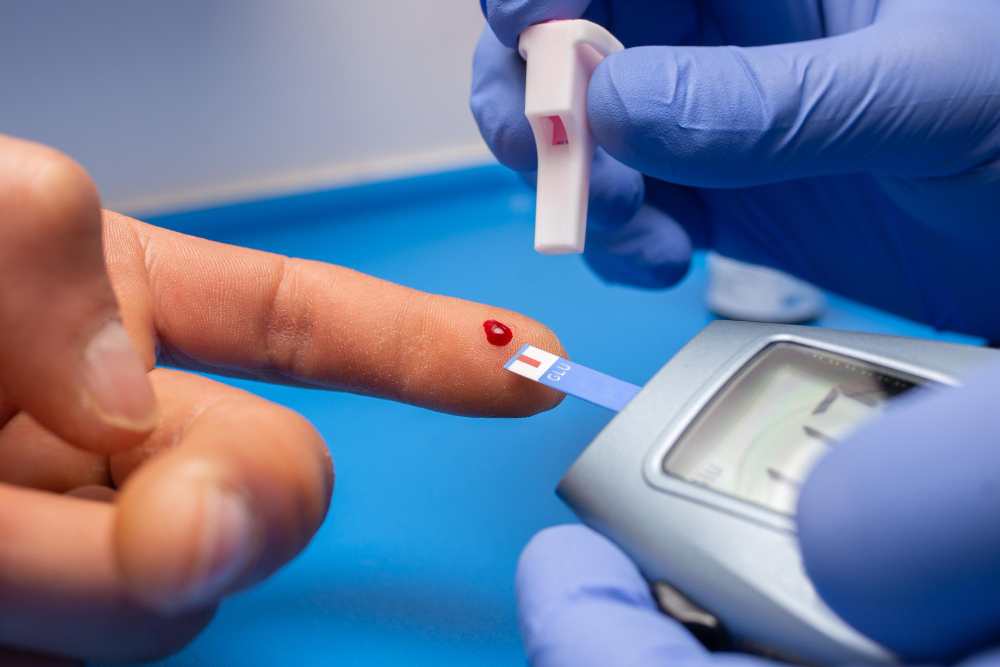
How Gestational Diabetes is Diagnosed
Doctors usually test for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. However, if you have risk factors, testing may happen earlier. The most common test is the glucose challenge test. Here’s how it works:
If your result is high, you may need a second test called the oral glucose tolerance test. This test checks how your body handles sugar over a few hours. Both tests help your doctor decide if you have gestational diabetes.
Treatment Options and Management
If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you can manage it with the right care. Treatment aims to keep your blood sugar in a healthy range. Your healthcare team will guide you. Common treatment options include:
With proper care, most women have healthy pregnancies and babies.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Gestational Diabetes
Making healthy choices every day can help control gestational diabetes. For example, you can:
Always follow your doctor’s advice for the best results.
Prevention Strategies
While you cannot always prevent gestational diabetes, you can lower your risk. Here are some helpful strategies:
Even small changes can make a big difference.
When to See a Doctor
If you are pregnant, regular prenatal visits are important. However, you should call your doctor if you notice:
Early care can help prevent problems for you and your baby. If you have questions about gestational diabetes symptoms or treatment, talk to your healthcare provider right away.
In summary, gestational diabetes is a common condition during pregnancy. With early diagnosis and proper care, you can manage it well. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice on gestational diabetes.